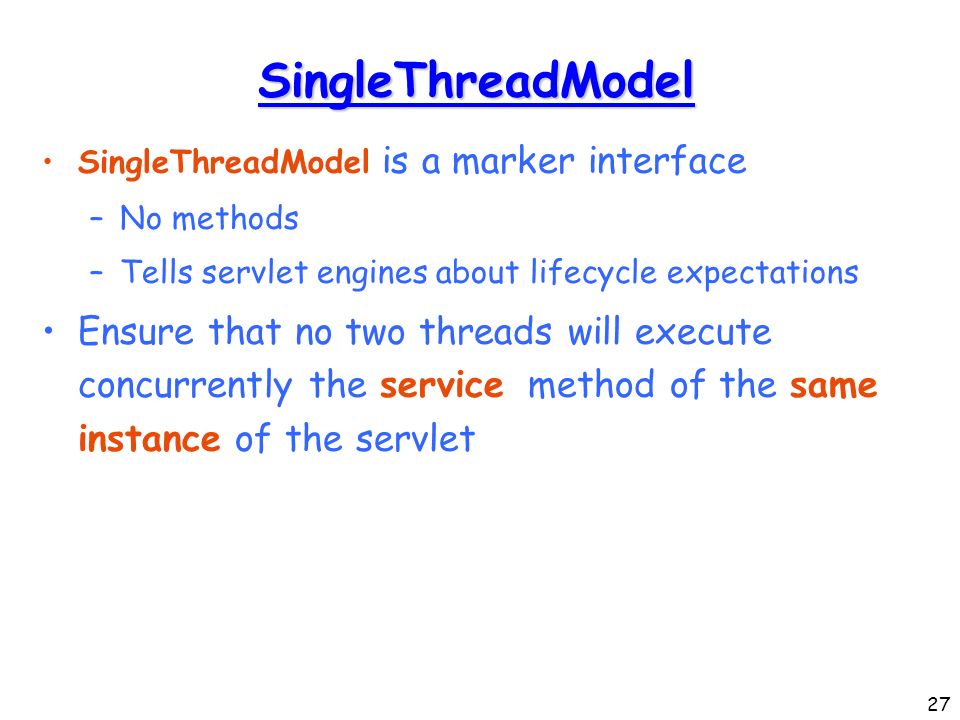
The RequestDispatcher interface provides the facility of dispatching the request to another resource it may be html, servlet or jsp. This interface can also be used to include the content of another resource also. It is one of the way of servlet collaboration.
There are two methods defined in the RequestDispatcher interface.
Methods of RequestDispatcher interface
The RequestDispatcher interface provides two methods. They are:
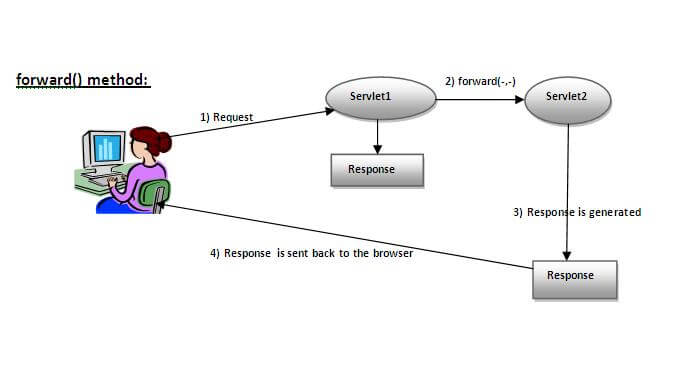
- public void forward(ServletRequest request,ServletResponse response)throws ServletException,java.io.IOException:Forwards a request from a servlet to another resource (servlet, JSP file, or HTML file) on the server.
- public void include(ServletRequest request,ServletResponse response)throws ServletException,java.io.IOException:Includes the content of a resource (servlet, JSP page, or HTML file) in the response.
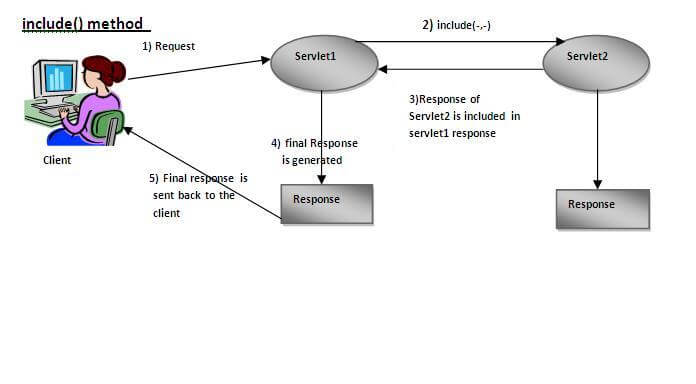
As you see in the above figure, response of second servlet is sent to the client. Response of the first servlet is not displayed to the user.
| As you can see in the above figure, response of second servlet is included in the response of the first servlet that is being sent to the client. |
How to get the object of RequestDispatcher
The getRequestDispatcher() method of ServletRequest interface returns the object of RequestDispatcher. Syntax:
Syntax of getRequestDispatcher method
public RequestDispatcher getRequestDispatcher(String resource);
Example of using getRequestDispatcher method
RequestDispatcher rd=request.getRequestDispatcher("servlet2");
//servlet2 is the url-pattern of the second servlet
rd.forward(request, response);//method may be include or forward
Example of RequestDispatcher interface
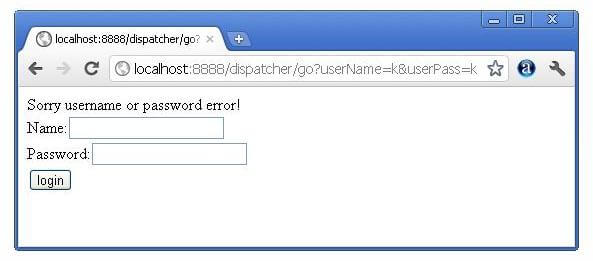
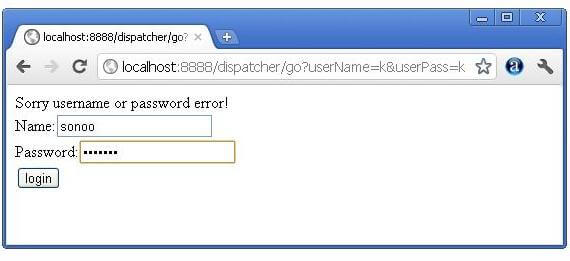
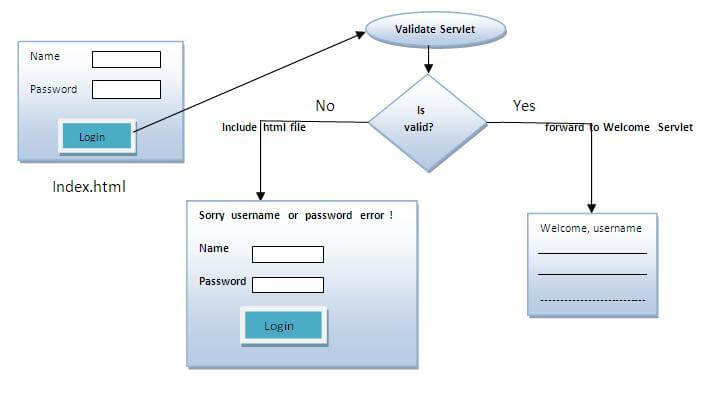
In this example, we are validating the password entered by the user. If password is servlet, it will forward the request to the WelcomeServlet, otherwise will show an error message: sorry username or password error!. In this program, we are cheking for hardcoded information. But you can check it to the database also that we will see in the development chapter. In this example, we have created following files:
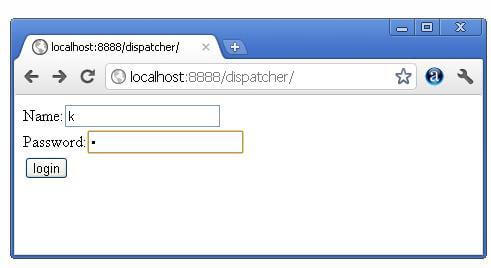
- index.html file: for getting input from the user.
- Login.java file: a servlet class for processing the response. If password is servet, it will forward the request to the welcome servlet.
- WelcomeServlet.java file: a servlet class for displaying the welcome message.
- web.xml file: a deployment descriptor file that contains the information about the servlet.
index.html
Login.java
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class Login extends HttpServlet {
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
String n=request.getParameter("userName");
String p=request.getParameter("userPass");
if(p.equals("servlet"){
RequestDispatcher rd=request.getRequestDispatcher("servlet2");
rd.forward(request, response);
}
else{
out.print("Sorry UserName or Password Error!");
RequestDispatcher rd=request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.html");
rd.include(request, response);
}
}
}
WelcomeServlet.java
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class WelcomeServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
String n=request.getParameter("userName");
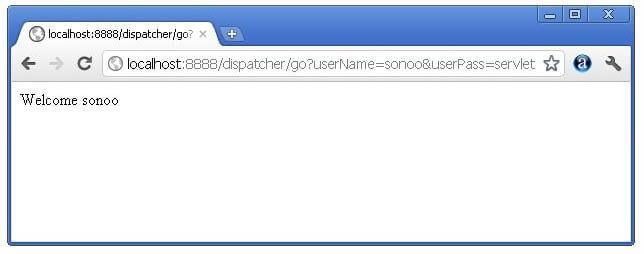
out.print("Welcome "+n);
}
}
web.xml
Login
Login
WelcomeServlet
WelcomeServlet
Login
/servlet1
WelcomeServlet
/servlet2
index.html





Leave A Comment