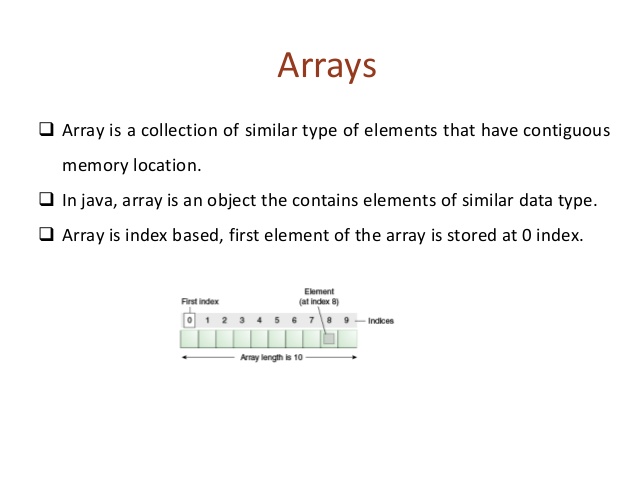
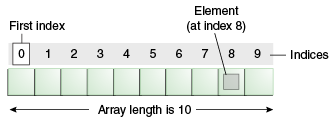
Normally, an array is a collection of similar type of elements that have a contiguous memory location.
Java array is an object which contains elements of a similar data type. It is a data structure where we store similar elements. We can store only a fixed set of elements in a Java array.
Array in java is index-based, the first element of the array is stored at the 0 index.
Advantages
- Code Optimization: It makes the code optimized, we can retrieve or sort the data efficiently.
- Random access: We can get any data located at an index position.
Disadvantages
- Size Limit: We can store only the fixed size of elements in the array. It doesn’t grow its size at runtime. To solve this problem, collection framework is used in Java which grows automatically.
Types of Array in java
There are two types of array.
- Single Dimensional Array
- Multidimensional Array
Single Dimensional Array in Java
Syntax to Declare an Array in Java
dataType[] arr; (or) dataType []arr; (or) dataType arr[];
Instantiation of an Array in Java
arrayRefVar=new datatype[size];
Example of Java Array
Let’s see the simple example of java array, where we are going to declare, instantiate, initialize and traverse an array.
//Java Program to illustrate how to declare, instantiate, initialize
//and traverse the Java array.
class Testarray{
public static void main(String args[]){
int a[]=new int[5];//declaration and instantiation
a[0]=10;//initialization
a[1]=20;
a[2]=70;
a[3]=40;
a[4]=50;
//traversing array
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)//length is the property of array
System.out.println(a[i]);
}}
Output:
10 20 70 40 50
Declaration, Instantiation and Initialization of Java Array
We can declare, instantiate and initialize the java array together by:
int a[]={33,3,4,5};//declaration, instantiation and initialization
Let’s see the simple example to print this array.
//Java Program to illustrate the use of declaration, instantiation
//and initialization of Java array in a single line
class Testarray1{
public static void main(String args[]){
int a[]={33,3,4,5};//declaration, instantiation and initialization
//printing array
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)//length is the property of array
System.out.println(a[i]);
}}
Output:
33 3 4 5
Passing Array to Method in Java
We can pass the java array to method so that we can reuse the same logic on any array.
Let’s see the simple example to get the minimum number of an array using a method.
//Java Program to demonstrate the way of passing an array
//to method.
class Testarray2{
//creating a method which receives an array as a parameter
static void min(int arr[]){
int min=arr[0];
for(int i=1;i<arr.length;i++) if(min>arr[i])
min=arr[i];
System.out.println(min);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int a[]={33,3,4,5};//declaring and initializing an array
min(a);//passing array to method
}}
Output:
3
Anonymous Array in Java
Java supports the feature of an anonymous array, so you don’t need to declare the array while passing an array to the method.
//Java Program to demonstrate the way of passing an anonymous array
//to method.
public class TestAnonymousArray{
//creating a method which receives an array as a parameter
static void printArray(int arr[]){
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++)
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
printArray(new int[]{10,22,44,66});//passing anonymous array to method
}}
Output:
10 22 44 66
Returning Array from the Method
We can also return an array from the method in Java.
//Java Program to return an array from the method
class TestReturnArray{
//creating method which returns an array
static int[] get(){
return new int[]{10,30,50,90,60};
}
public static void main(String args[]){
//calling method which returns an array
int arr[]=get();
//printing the values of an array
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++)
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}}
Output:
10 30 50 90 60
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) throws an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if length of the array in negative, equal to the array size or greater than the array size while traversing the array.
//Java Program to demonstrate the case of
//ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException in a Java Array.
public class TestArrayException{
public static void main(String args[]){
int arr[]={50,60,70,80};
for(int i=0;i<=arr.length;i++){
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}}
Output:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 4 at TestArrayException.main(TestArrayException.java:5) 50 60 70 80
Multidimensional Array in Java
In such case, data is stored in row and column based index (also known as matrix form).
Syntax to Declare Multidimensional Array in Java
dataType[][] arrayRefVar; (or) dataType [][]arrayRefVar; (or) dataType arrayRefVar[][]; (or) dataType []arrayRefVar[];
Example to instantiate Multidimensional Array in Java
int[][] arr=new int[3][3];//3 row and 3 column
Example to initialize Multidimensional Array in Java
arr[0][0]=1; arr[0][1]=2; arr[0][2]=3; arr[1][0]=4; arr[1][1]=5; arr[1][2]=6; arr[2][0]=7; arr[2][1]=8; arr[2][2]=9;
Example of Multidimensional Java Array
Let’s see the simple example to declare, instantiate, initialize and print the 2Dimensional array.
//Java Program to illustrate the use of multidimensional array
class Testarray3{
public static void main(String args[]){
//declaring and initializing 2D array
int arr[][]={{1,2,3},{2,4,5},{4,4,5}};
//printing 2D array
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}}
Output:
1 2 3 2 4 5 4 4 5
Jagged Array in Java
If we are creating odd number of columns in a 2D array, it is known as a jagged array. In other words, it is an array of arrays with different number of columns.
//Java Program to illustrate the jagged array
class TestJaggedArray{
public static void main(String[] args){
//declaring a 2D array with odd columns
int arr[][] = new int[3][];
arr[0] = new int[3];
arr[1] = new int[4];
arr[2] = new int[2];
//initializing a jagged array
int count = 0;
for (int i=0; i<arr.length; i++)
for(int j=0; j<arr[i].length; j++)
arr[i][j] = count++;
//printing the data of a jagged array
for (int i=0; i<arr.length; i++){
for (int j=0; j<arr[i].length; j++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();//new line
}
}
}
Output:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
What is the class name of Java array?
In Java, an array is an object. For array object, a proxy class is created whose name can be obtained by getClass().getName() method on the object.
//Java Program to get the class name of array in Java
class Testarray4{
public static void main(String args[]){
//declaration and initialization of array
int arr[]={4,4,5};
//getting the class name of Java array
Class c=arr.getClass();
String name=c.getName();
//printing the class name of Java array
System.out.println(name);
}}
Output:
I
Copying a Java Array
We can copy an array to another by the arraycopy() method of System class.
Syntax of arraycopy method
public static void arraycopy( Object src, int srcPos,Object dest, int destPos, int length )
Example of Copying an Array in Java
//Java Program to copy a source array into a destination array in Java
class TestArrayCopyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//declaring a source array
char[] copyFrom = { 'd', 'e', 'c', 'a', 'f', 'f', 'e',
'i', 'n', 'a', 't', 'e', 'd' };
//declaring a destination array
char[] copyTo = new char[7];
//copying array using System.arraycopy() method
System.arraycopy(copyFrom, 2, copyTo, 0, 7);
//printing the destination array
System.out.println(String.valueOf(copyTo));
}
}
Output:
caffein
Addition of 2 Matrices in Java
Let’s see a simple example that adds two matrices.
//Java Program to demonstrate the addition of two matrices in Java
class Testarray5{
public static void main(String args[]){
//creating two matrices
int a[][]={{1,3,4},{3,4,5}};
int b[][]={{1,3,4},{3,4,5}};
//creating another matrix to store the sum of two matrices
int c[][]=new int[2][3];
//adding and printing addition of 2 matrices
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
c[i][j]=a[i][j]+b[i][j];
System.out.print(c[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();//new line
}
}}
Output:
2 6 8 6 8 10
Multiplication of 2 Matrices in Java
In the case of matrix multiplication, a one-row element of the first matrix is multiplied by all the columns of the second matrix which can be understood by the image given below.

Let’s see a simple example to multiply two matrices of 3 rows and 3 columns.
//Java Program to multiply two matrices
public class MatrixMultiplicationExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
//creating two matrices
int a[][]={{1,1,1},{2,2,2},{3,3,3}};
int b[][]={{1,1,1},{2,2,2},{3,3,3}};
//creating another matrix to store the multiplication of two matrices
int c[][]=new int[3][3]; //3 rows and 3 columns
//multiplying and printing multiplication of 2 matrices
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
c[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<3;k++)
{
c[i][j]+=a[i][k]*b[k][j];
}//end of k loop
System.out.print(c[i][j]+" "); //printing matrix element
}//end of j loop
System.out.println();//new line
}
}}
Output:
6 6 6 12 12 12 18 18 18





Leave A Comment