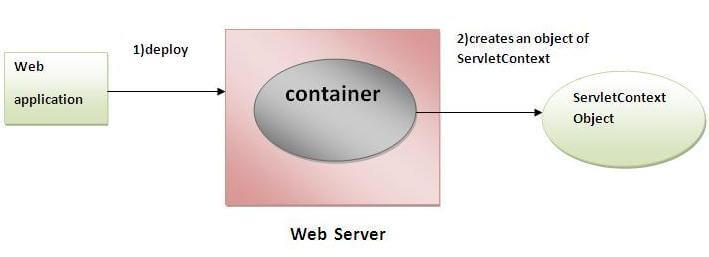
An object of ServletContext is created by the web container at time of deploying the project. This object can be used to get configuration information from web.xml file. There is only one ServletContext object per web application.
If any information is shared to many servlet, it is better to provide it from the web.xml file using the <context-param> element.
Advantage of ServletContext
Easy to maintain if any information is shared to all the servlet, it is better to make it available for all the servlet. We provide this information from the web.xml file, so if the information is changed, we don’t need to modify the servlet. Thus it removes maintenance problem.
Usage of ServletContext Interface
There can be a lot of usage of ServletContext object. Some of them are as follows:
- The object of ServletContext provides an interface between the container and servlet.
- The ServletContext object can be used to get configuration information from the web.xml file.
- The ServletContext object can be used to set, get or remove attribute from the web.xml file.
- The ServletContext object can be used to provide inter-application communication.
Commonly used methods of ServletContext interface
There is given some commonly used methods of ServletContext interface.
|
How to get the object of ServletContext interface
- getServletContext() method of ServletConfig interface returns the object of ServletContext.
- getServletContext() method of GenericServlet class returns the object of ServletContext.
Syntax of getServletContext() method
public ServletContext getServletContext()
Example of getServletContext() method
//We can get the ServletContext object from ServletConfig object ServletContext application=getServletConfig().getServletContext(); //Another convenient way to get the ServletContext object ServletContext application=getServletContext();
Syntax to provide the initialization parameter in Context scope
| The context-param element, subelement of web-app, is used to define the initialization parameter in the application scope. The param-name and param-value are the sub-elements of the context-param. The param-name element defines parameter name and and param-value defines its value. |
......
parametername
parametervalue
......
Example of ServletContext to get the initialization parameter
| In this example, we are getting the initialization parameter from the web.xml file and printing the value of the initialization parameter. Notice that the object of ServletContext represents the application scope. So if we change the value of the parameter from the web.xml file, all the servlet classes will get the changed value. So we don’t need to modify the servlet. So it is better to have the common information for most of the servlets in the web.xml file by context-param element. Let’s see the simple example: |
DemoServlet.java
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class DemoServlet extends HttpServlet{
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse res)
throws ServletException,IOException
{
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter pw=res.getWriter();
//creating ServletContext object
ServletContext context=getServletContext();
//Getting the value of the initialization parameter and printing it
String driverName=context.getInitParameter("dname");
pw.println("driver name is="+driverName);
pw.close();
}}
web.xml
sonoojaiswal DemoServlet dname sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver sonoojaiswal /context
Example of ServletContext to get all the initialization parameters
| In this example, we are getting all the initialization parameter from the web.xml file. For getting all the parameters, we have used the getInitParameterNames() method in the servlet class. |
DemoServlet.java
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class DemoServlet extends HttpServlet{
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse res)
throws ServletException,IOException
{
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out=res.getWriter();
ServletContext context=getServletContext();
Enumeration e=context.getInitParameterNames();
String str="";
while(e.hasMoreElements()){
str=e.nextElement();
out.print("
"+context.getInitParameter(str));
}
}}
web.xml
sonoojaiswal DemoServlet dname sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver username system password oracle sonoojaiswal /context





Leave A Comment