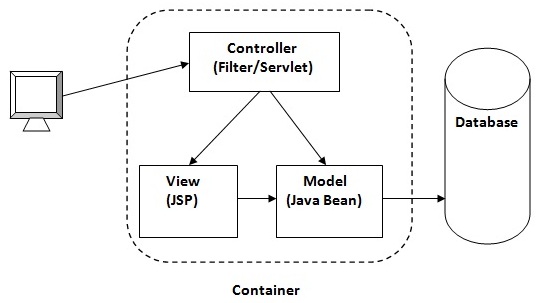
MVC stands for Model View and Controller. It is a design pattern that separates the business logic, presentation logic and data.
Controller acts as an interface between View and Model. Controller intercepts all the incoming requests.
Model represents the state of the application i.e. data. It can also have business logic.
View represents the presentaion i.e. UI(User Interface).
Advantage of MVC (Model 2) Architecture
- Navigation Control is centralized
- Easy to maintain the large application
MVC Example in JSP
In this example, we are using servlet as a controller, jsp as a view component, Java Bean class as a model.
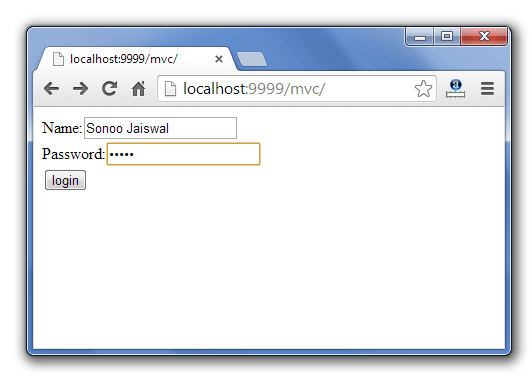
In this example, we have created 5 pages:
- index.jsp a page that gets input from the user.
- ControllerServlet.java a servlet that acts as a controller.
- login-success.jsp and login-error.jsp files acts as view components.
- web.xml file for mapping the servlet.
File: ControllerServlet
package com.javatpoint;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class ControllerServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out=response.getWriter();
String name=request.getParameter("name");
String password=request.getParameter("password");
LoginBean bean=new LoginBean();
bean.setName(name);
bean.setPassword(password);
request.setAttribute("bean",bean);
boolean status=bean.validate();
if(status){
RequestDispatcher rd=request.getRequestDispatcher("login-success.jsp");
rd.forward(request, response);
}
else{
RequestDispatcher rd=request.getRequestDispatcher("login-error.jsp");
rd.forward(request, response);
}
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req, resp);
}
}
File: LoginBean.java
package com.javatpoint;
public class LoginBean {
private String name,password;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public boolean validate(){
if(password.equals("admin")){
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
}
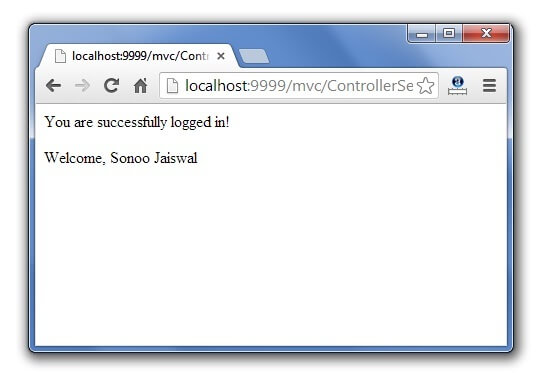
File: login-success.jsp
<%@page import="com.javatpoint.LoginBean"%>
You are successfully logged in!
<% LoginBean bean=(LoginBean)request.getAttribute(“bean”); out.print(“Welcome, “+bean.getName()); %>
File: login-error.jsp
Sorry! username or password error
<%@ include file=”index.jsp” %>
File: web.xml
s1
com.javatpoint.ControllerServlet
s1
/ControllerServlet







Leave A Comment